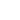
What's the difference between magnetic flux density, magnetic flux and residual flux density?
What's the difference between magnetic flux density, magnetic flux and residual flux density?
When I was new to this industry, I have confusions between magnetic flux density, magnetic flux and residual flux density.
So, what's the meaning and difference between them?
Magnetic Flux
Density: lines of flux per unit area, usually measured in Gauss (CGS). One line
of flux per square centimeter is one Maxwell.
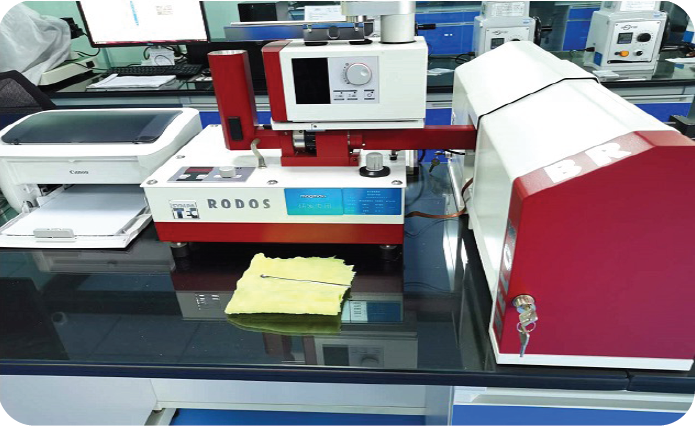
Gaussmeter
Surface magnetic flux density refers to a measurement point, actually, it is the value of a small measurement area, and the magnetic field distribution of the magnet changes, so the surface magnetism at different points is generally different. For applications that require the use of space magnetic fields, surface magnetic flux density or the magnetic induction intensity value at a specified point is usually regarded as an important technical requirement.
The surface magnetism is related to the height-to-diameter ratio of the magnet (the ratio of the height to the diameter of the magnet. The default height or thickness here is the magnetization direction of the magnet). The greater the height-to-diameter ratio, the higher the surface magnetism, that is, the greater the surface area perpendicular to the magnetization direction., the lower the surface magnetism; the larger the size of the magnetization direction, the higher the surface magnetism. In addition, the Hall elements on the Gaussmeters of different manufacturers are different, and the surface magnetism measured for the same magnet is also slightly different.
Magnetic Flux - Is a contrived but measurable concept that has evolved in an attempt to describe the “flow” of a magnetic field. When the magnetic induction, B, is uniformly distributed and is normal to the area, A, the flux, Ø = BA.
Fluxmeter
The measuring instrument for magnetic flux is a flux meter. With the Helmholtz coil, it can not only measure the magnetic flux, but also calculate its magnetic moment, because the measured value of the magnetic flux will change with the parameters of the flux meter and the Helmholtz coil. Variety. Magnetic flux and magnetic moment are more like the difference between weight and mass. Weight is affected by the gravitational constant. The weight of the same object on Earth and Mars is different, but the mass is the same. Affected by the number of turns of the coil, the magnetic flux of the same magnet measured by different flux meters and coils may be different, but the magnetic moment must be the same.
When the magnet is in an open-circuit state, the actual residual magnetization value Bdi (also called essential magnetic flux density) corresponding to the operating point can be calculated by converting magnetic flux into magnetic moment. Bdi=Φ*coil constant/magnet volume.
Residual magnetic flux density, surface magnetic flux density and magnetic flux are three concepts that are easily confused. Let’s clarify them here:
• Residual magnetism is an essential property of materials. As long as self-demagnetization does not occur, the residual magnetism of a magnet remains unchanged. It is determined by the product's raw material formula and preparation process. The test is conducted in a completely closed circuit state.
• Surface magnetic flux density is the magnetic induction intensity value at the measurement location (a small area) when the magnet or magnetic component is in an open circuit or semi-open circuit state. Surface magnetic flux density is a directional vector, and the surface magnetic flux density data on different surfaces of the magnet are very different. We usually refer to the surface magnetic flux density value perpendicular to the magnetic pole surface. The maximum surface magnetic flux density of a single magnet is one-half of the residual magnetic flux density. Note that it is a "single magnet". In some magnetic components and magnet arrays, special magnetic circuit designs can be used to increase the magnet's surface magnetism. Its value can even exceed the remanence.
• Magnetic flux is the overall magnetic size of the magnet measured through coil testing. Usually, magnetic assemblies are not suitable for testing magnetic flux. Magnetic flux also has direction requirements by default. Of course, the total magnetic flux value can also be measured using a three-dimensional Helmholtz coil during actual measurement. Special attention needs to be paid to the test direction when measuring surface magnetism and magnetic flux.
Hangzhou Vector Magnets tests from appearance to function to ensure quality from raw material to end product.