Electrophoresis
What is electrophoresis?
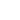
The electrophoretic coating is to immerse the parts in a
water-soluble electrophoresis bath, insert the anode and cathode electrodes
into the bath at the same time, and apply a direct current between the two
electrodes to produce an electrochemical reaction, so that the water-soluble
paint is evenly deposited on the parts, forming an anti-corrosion coating
composed of resin particles, or a high-molecular polymer anti-corrosion layer.
Electrophoretic coating not only has good bonding force with
porous magnet surface, but also has corrosion resistance such as salt spray, acid,
and alkali resistance.
Compared with spray coating, it has the following advantages:
1. High coating utilization rate. During the spraying process, a
large amount of spray paint is scattered, and about half of the paint is lost.
However, the use of ultrafiltration technology in electrophoretic coating can
make the paint utilization rate reach 90%-95%.
2. Electrophoretic paint is water-soluble paint, no organic solvent
is needed, energy and raw materials are saved, and environmental pollution is
reduced.
3. High production efficiency. After pretreatment, the bonded
magnet parts can be electrophoresed directly without drying, shortening the
coating time.
4. Good coating effect for complex parts. Electrophoretic
coating relies on the distribution of the electric field in the electrophoresis
bath for electrodeposition. Since the deposited coating film is insulating, a
uniform coating can be formed on all parts of the part.
5. The coating quality is good, the corrosion resistance is
strong, and the bonding force is good.
Electrophoretic coating also has disadvantages:
1. The one-time investment cost is high, the maintenance and
management of the electrophoresis bath is complicated, and various process
parameters need to be carefully controlled.
2. Electrophoretic coating cannot cover up the defects of the
magnet surface, such as cavities, scratches, dents, etc., so the surface
conditions of the product are relatively high.
3. Hooking and unhooking require more manual labor.
Classification of electrophoretic coating
Put the electrophoretic paint in the electrophoresis tank,
including polymer resin, organic solvent, color suspended particles and water,
etc., and stir them to form a uniform solution.
Electrophoretic coating has two types: anode coating and cathode
coating. Anodic electrophoresis uses a sintered NdFeB magnet as the anode. In
this way, the base metal and surface treatment film (such as phosphating film)
are precipitated and dissolved at the same time during the electrophoresis
process, which reduces the corrosion resistance of the electrophoretic
deposited film. Therefore, in most cases Cathodic electrophoresis is used, that
is, sintered NdFeB is used as the cathode, and cationic electrophoretic paint
is used. This paint is a water-soluble coating formed by neutralizing synthetic
resins containing amino groups with organic acids.
The cathodic electrophoresis layer uses organic acid as a
neutralizer, which has low toxicity. The mechanical strength of the wet paint
film itself and the bonding force with the workpiece are higher than that of
the anode electrophoretic coating. However, the cost of cathodic
electrophoretic coating is high, and the electrophoresis bath is acidic, which
has a corrosive effect on equipment. The cathodic electrophoresis tank should
be made of corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel or
acid-resistant plastics.
Process flow of sintered NdFeB electrophoretic coating
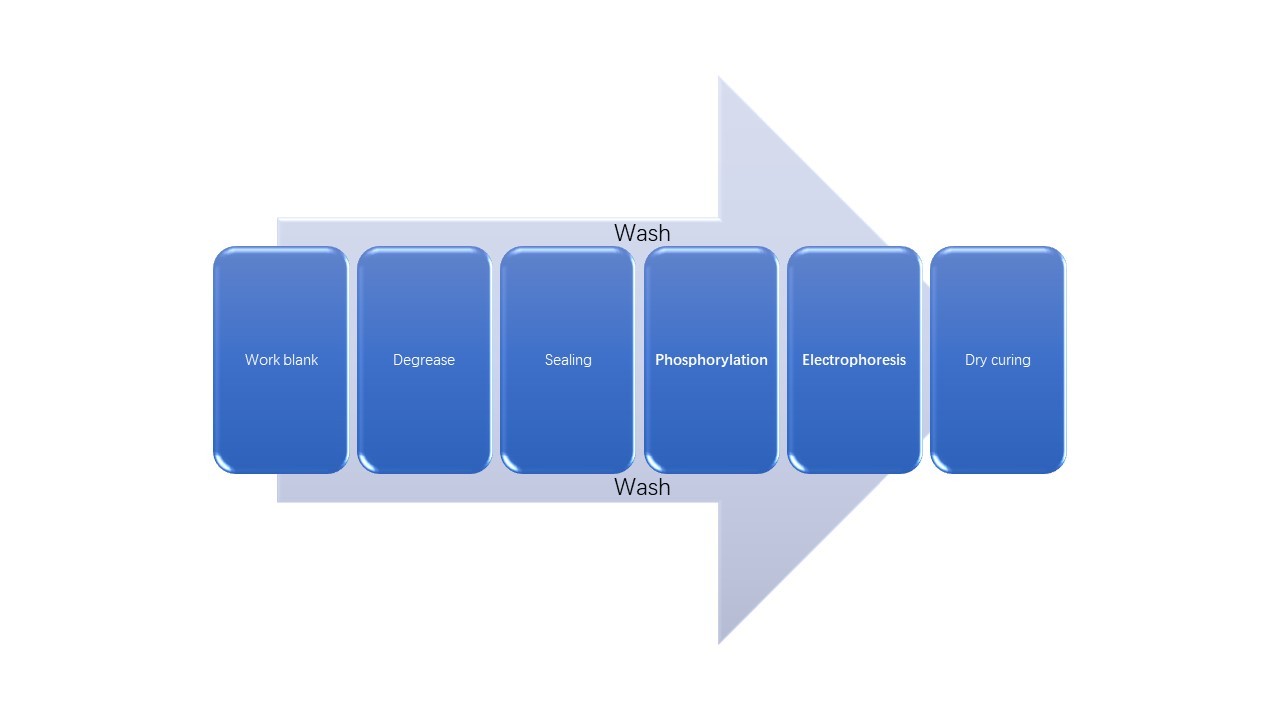
The process flow of electrophoretic coating is mainly divided
into three parts: surface pretreatment, electrophoresis and drying and curing.
Smooth and clean surface is the basis of high-quality
electrophoretic coating, and the purpose of surface treatment is to create good
surface conditions. The electrophoretic coating process is a complex chemical
change process. As the coating is continuously deposited on the surface of the
magnet, the composition of the electrophoresis tank is constantly changing. The
solid components, the pH value of the electrophoresis tank, temperature,
electrophoresis voltage, Electrode spacing, etc.