Some introductions of rare earth functional materials
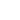
Rare earth elements refer to 15 lanthanide
oxides with atomic numbers 57-71 in the periodic table, as well as 17 elements
of Sc and Y with similar chemical properties of lanthanides. These 17 elements
are divided into LREE and HREE .
Due to the atomic structure of the 4f electron layer, rare earth elements are extremely rich in electronic energy levels, have special properties such as light, electricity, magnetism, and nucleus, and can form a wide variety of new materials with specific properties and other materials.
Rare earth functional materials can be divided into rare earth permanent magnet materials, rare earth luminescent materials, rare earth hydrogen storage materials, rare earth catalytic materials, rare earth polishing materials and so on.
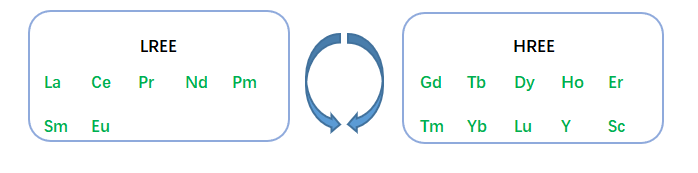
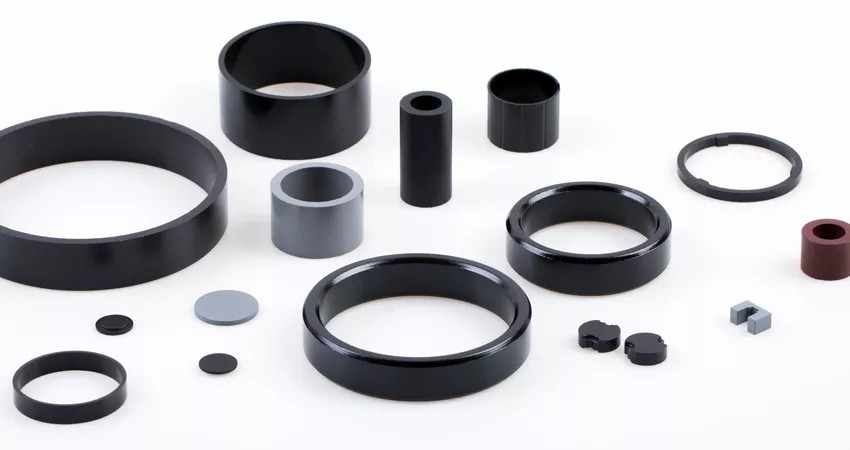
Rare earth permanent magnetic material is a
kind of magnetic material made by alloying Sm, Nd mixed rare earth metals and
transition metals (such as Co, Fe), pressed and sintered by powder metallurgy
method, and magnetized by a magnetic field.
In 1967, StrNa discovered the first
generation of rare earth permanent magnet SmCo5
In 1977, Ojima discovered the first
generation of rare earth permanent magnet Sm2Co17
In 1983, Sagawa discovered the
third-generation rare earth permanent magnet Nd2Fe14B

2. Rare earth luminescent materials
Rare earth luminescent materials refer to a
new generation of luminescent materials made of rare earth elements as
activators or matrix components. There are 4f orbitals in the electron
configuration of rare earth element atoms. When 4f electrons radiatively
transition from a high energy level to a low energy level, they emit light of
different wavelengths.
According to the different excitation light
sources, rare earth luminescent materials can be divided into: photoluminescent
materials, cathodoluminescent materials, X-ray luminescent materials,
electroluminescent materials and so on.

3. Rare earth hydrogen storage materials
Rare earth hydrogen storage material
generally refers to rare earth hydrogen storage alloy powder, which is a
material that can reversibly absorb and release hydrogen at a lower temperature
after adding some second metal to the rare earth metal to form an alloy.
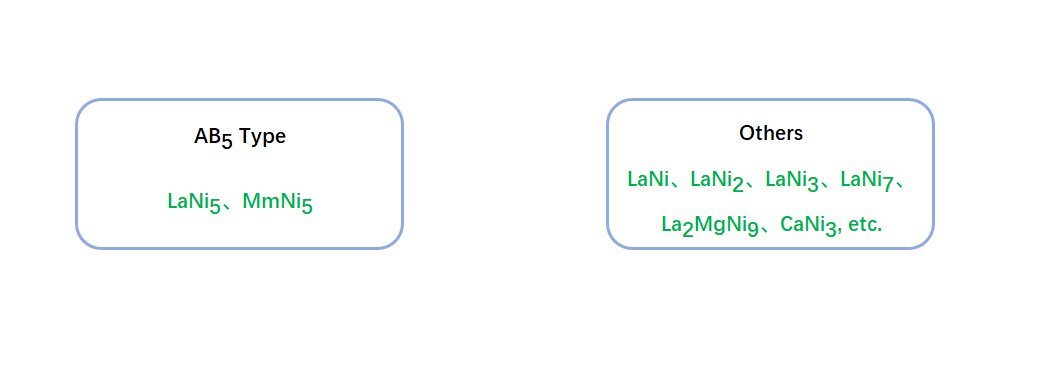
According to the structure type, rare earth
hydrogen storage materials can be divided into two categories: AB5 (LaNi5)
hydrogen storage alloys and non-AB5 type rare earth hydrogen storage alloys.
4. Rare earth polishing materials
Rare earth polishing material mainly refers
to rare earth polishing powder, which refers to a mixed light rare earth oxide
powder with cerium oxide as the main component to improve the surface finish of
products or parts.
Generally can be divided into low cerium
polishing powder, medium cerium polishing powder, high cerium polishing powder.
Rare earth polishing powder is widely used in the polishing of optical glass
parts, TV kinescope glass bulbs, spectacle lenses, flat glass, oscilloscope
tubes and organic glass.

Application fields of rare earth
functional materials
Metallurgy
Graphite spheroidizing agent, nucleating
agent, harmful element control used in cast iron to improve the quality of cast
iron.
Glass And Ceramics
Glass: coloring
agent, decoloring agent, polishing agent
Ceramics: reduce
the chipping of glaze
Military
Improve the tactical performance of
weapons can also be used as a lubricant in the nuclear industry.
Petrochemical
At present, 90% of the world's oil
refinery and cracking units use catalytic cracking agents containing rare earths.
Agriculture:
Growth and physiological regulators
enhance the ability of crops to resist drought and flood.